Gear
A gear is a toothed cylindrical or roller shape component of a machine which meshes with another toothed cylindrical to transmit power from one shaft to another. It is mainly used to change in torque and speed of the driving shaft and the driven shaft.
Principle of gear
It works on the basic principle that energy is neither be created nor destroyed; it can be converted into one form to another.
We know that power is the function of speed and torque or we can say that power is the product of torque and speed (P = TV) of the shaft. So when we connect a small gear on the driving shaft and a larger gear on the driven shaft, the speed decreases of the driven shaft per unit rotation of the driving shaft.
Because the power is conservative so according to this the torque of driven shaft increase according to the ratio of driving gear to driven gear or according to the ratio of driving velocity to drive velocity. So by use of various sizes of gears, we can obtain any combinations of torque and speed of driven member.
We know that power is the function of speed and torque or we can say that power is the product of torque and speed (P = TV) of the shaft. So when we connect a small gear on the driving shaft and a larger gear on the driven shaft, the speed decreases of the driven shaft per unit rotation of the driving shaft.
Because the power is conservative so according to this the torque of driven shaft increase according to the ratio of driving gear to driven gear or according to the ratio of driving velocity to drive velocity. So by use of various sizes of gears, we can obtain any combinations of torque and speed of driven member.
1. Spur Gear:-
- It has straight teeth parallel to the axis of the wheel or shaft.
- It is used to transmit power between parallel shafts.
- Only one tooth of the spur gear meshes at a time.
- It is regularly used for speed reduction or increase, resolution and accuracy enhancement for positioning systems, torque multiplication.
- It creates noise during its operation.
- when it meshes with another spur gear it transmits the power in the parallel shaft and when it connects with the helical gear it will transmit power at an angle from the driving axis.
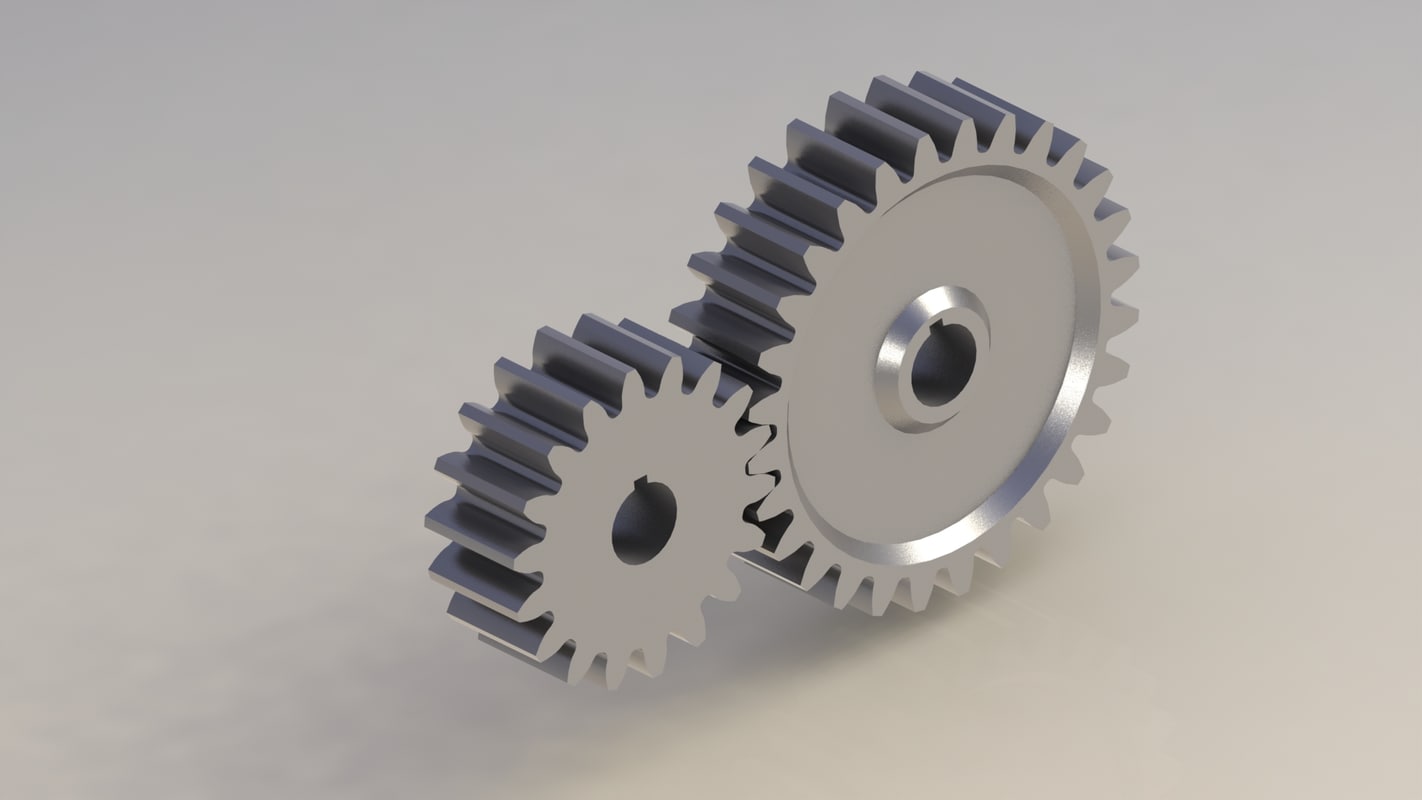
2. Helical Gear-
- On the helical gears, teeth are cut at an angle from the axis of it.
- This is a cylindrically shaped gear with helicoid teeth.
- It has less wear and tear due to which they are widely used in industries.
- It is used for transmitting power in the parallel shaft but sometimes they are used to transmit power in the non-parallel shaft also.
- The main advantage of helical gears is that they work with less noise and vibration because the load is distributed in the full helix as compared to spur gears.
A disadvantage is the axial thrust force caused due to the helix form.

3. Double helical Gear:-
Its operation is smoother and quieter as compared with the spur gear.
It is most commonly used in transmission gearboxes.
This gear is used to provide an additional shear area on gear which further required for higher torque transmission.
it decreases the noise problem.

4. Bevel/Miter Gear:-
- This gear is used for transmitting the power in two or more different directions about a gear.
- This gear is used to transmit power between perpendiculars.
- The driving shaft and driven shaft make a right angle with each other and both the axis of the shaft meets each other at one point.

a. Spiral Bevel gears:-
- These gears are mounted on a shaft whose axes are intersecting.
- The pitch surface is conical. Spiral bevel gears have curved oblique teeth (spiral), which allow contact to develop gradually and smoothly.
- They have more contact length and area and less power transmission efficiency compared to straight bevel gears.
- They are useful for high-speed applications and others requiring less noise and vibration.
- They are difficult to design and costly to manufacture, as they require specialized and sophisticated machinery for their manufacture.
- They produce more thrust load on shaft bearings than straight bevel gears
- Longer contact length and larger contact ratio compared to straight bevel gears of the same size.

b) Zero Bevel gear:-
Zerol bevel gears are spiral bevel gears in which the spiral angle is zero in the middle of the face width. They have the combination of advantages of straight and spiral bevel gears.
Their characteristics are-
Their characteristics are-
- The force on the teeth of zero bevel gears is the same as straight bevel gears.
- Since zero bevel gears can be ground, compared to straight bevel gears, they are more accurate, quiet and have a superior anti-friction quality.
- As with spiral bevel gears, they are used with a right-hand and left-hand twist as a set.
- Normally, spiral bevel gears can be rotated only in one direction, but due to the zero twist angle of zero gears, they can be rotated in both directions just as with straight bevel gears.
*zero bevel gears are stronger against breakage compared to straight and spiral bevel gears.
The reason for strength-
- Tooth thickness is larger.
- The tooth length of zero bevel gears is longer than those of straight bevel gears.

5. Worm Gear:-
A worm gear is an arrangement of two gears in which one gear is called as worm ( gear in the form of the screw) meshes with a worm gear ( similar as spur gear). The two elements are called the worm screw and the worm wheel. Worm gears are used in presses, rolling mills, on rudders and worm drive saws, etc.- Worm gears are used to transmit power between two nonintersecting shafts, which are right angles to each other.
- They are limited in their load transmission capacity.
- Worm gear drives are used for a large speed reduction ratio of 100:1 or more in a single stage.
- The pair of teeth on meshing worm and worm gear must have the same hand.

6) Rack and Pinion:-
Sometimes what happens, the gears of a shaft meshes externally and internally with the gears in a straight line (i.e. straight line is also defined as the wheel of infinite radius). Such type of gear is known as rack and pinion. In a rack and pinion types of gears, the straight line gear is called rack and the circular gear is called pinion.- This gear is used in a steering system of an automobile.
- Rack and pinion are used to convert rotary motion to translating motion or vice versa.
- They have more contact length and area and less power transmission efficiency compared to straight bevel gears.
- They are useful for high-speed applications and others requiring less noise and vibration.
- They produce more thrust load on shaft bearings than straight bevel gears.







0 Comments
Thank for Visiting our site
we will Happy to see you here again