Heat affected zone
The region up to which component is subjected to uncontrolled heat treatment is known as the heat-affected zone.
It is the region or area nearby the weld bead which is subjected to uncontrolled heat treatment heating or cooling.
when high-temperature molten metal deposited in the gap the temperature near the end of the workpiece increases to the high value. At the end of the workpiece as the material has not melted out it will not acquire the property of solidified weld metal. since elevated/high temperature is maintained for the longer period of time the property of end of the workpiece will not be similar to the property of the base metal. it means the 3rd zone has been found over the workpiece where property neither matches with workpiece nor it matches with the solidified base metal.
In most cases steel is available as a workpiece in the welding operation and due to faster cooling rate hard and brittle martensite formation takes place near the end of the workpiece. since martensite is very strong in compression and very weak in the tension and generally welded structures are designed for tensile loading the strength of heat affected zone is minimum in tensile loading.
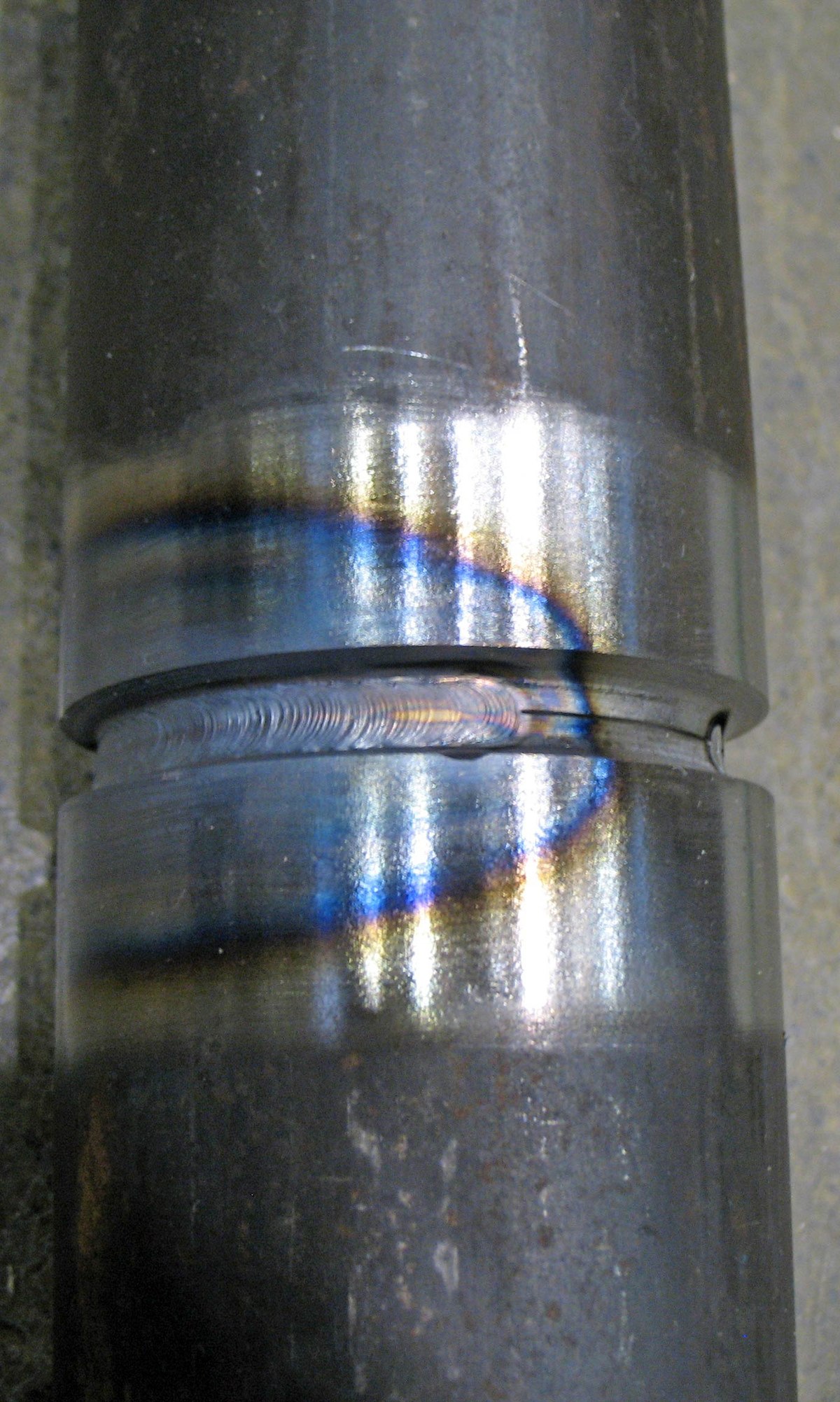 |
| The physical appearance of HAZ |
 |
| Location of HAZ |
Factor affecting the heat
The factor with increase the heat contained in the workers will increase the heat-affected zone
welding speed
welding is performed at the high speed of the workpiece is heated for a sorted period of time in which it contains in the workpiece will be less which leads to a decrease in the heat-affected zone.
Thermal conductivity of base metal
If the material having higher thermal conductivity according to the Furious law of heat conduction more amount of heat transmitted which increased the heat content in workpiece will increase the heat-affected zone
starting temperature
In many cases to avoid the bending or distortion of what is material with need to be preheated because of preheating the starting temperature of what is material increase with increase heat contents in the workpiece, therefore, it increases the heat-affected zone.
The thickness of workpiece material
According to Fourier law of heat conduction heat transfer is inversely proportional to length if we increase the thickness of workers material due to the decrease in heat content heat affected zone will decrease.
*Note- In case of electron beam welding (EBW) electron beam is concentrated form of energy heat affected zone will be minimal over the walking in this case of plasma arc welding because very high-temperature plasma heat-affected zone is maximum.






0 Comments
Thank for Visiting our site
we will Happy to see you here again