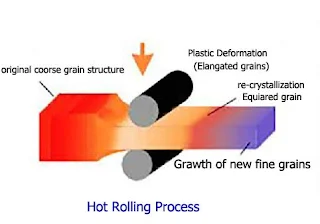
Hot working process
It is a process in which the material is heated above its re-crystallization temperature but below the melting temperature of the material. less amount of power is required for deforming the metal in hot working as compared to cold working.Re-crystallization temperature of Fe= 450°c
But the melting temperature is approx 1500°c
Cold working
The process of forming in which the metal is heated below its re-crystallization temperature is known as cold working. It gives less finished surface compared to hot working.E.g.- In cold working, Fe is heated below the 450°c.
Example- rolling at normal temperature,
Extrusion at normal temperature etc.
Advantage of hot working
- No strain hardening because the working temperature is above its re-crystallization temperature
- No chance of porosity in the material.
- As shear stress gets reduced at a higher temperature, therefore, less force is required for defamation purposes.
- Ductility and impact resistance are improved
- A very large workpiece can be deformed with reasonable size equipment.
- When course-sized grains are refined they result in a fine grain structure.
- Further stress removal process is not required.
- High reduction is possible without any fracture.
Disadvantage
- Due to high-temperature cooling handling of hot metal is costly and difficult
- Due to high temperature, there is a scaling of surface which leads to the poor surface finish of the finished product
- Close tolerance of dimensions is not possible
- Brittle material can't be hard work
- Metallurgical structure of workpiece may be non-uniform.
- example -hot rolling,hot extrusion,hot forging etc.
Advantages of cold working
- Increased strength
- Improved surface finish
- Controlled dimensional tolerance and concentricity
- Improved straightness
- Improved machinability
Disadvantages of cold working-
- Higher forces are required to initiate and complete the deformation
- Less ductility is available
- Intermediate anneals may be required to compensate for the loss of ductility that accompanies strain hardening
- Heavier and more powerful equipment is required
- Metal surfaces must be clean and scale-free
- Imparted directional properties may be detrimental
- Undesirable residual stresses may be produced







1 Comments
Add some more topic about mechanical engineering.
ReplyDeleteThank for Visiting our site
we will Happy to see you here again