Radiation-
The radiation is the emission of energy as electromagnetic waves. It carries heat energy in the form of packets of energy.These packets are called photons. Each photon is a discrete entity of electromagnetic radiation
Blackbody-
A blackbody is a hypothetical/idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence.Emissivity
The emissivity of a surface is defined as the ratio of the radiation emitted by the surface to the radiation emitted by a blackbody at the same temperature. Thus,
0 ≤ ε ≤ 1
The total emissivity of a surface is the average emissivity of a surface over all
direction and wavelengths:
Total Emissivity-
It is defined as the ratio between the total hemispherical power of the non-black body and the total emissive power of the black body at the same temperature.
Type of surfaces
- White body
The surface that reflects all the incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions.
- Black body
The body which absorbs all the incident radiation on it.
- Gray body-
it is a surface which its properties are independent of wavelength.
- Opaque/Diffuse body-
Absorptivity α: it is the fraction of irradiation absorbed by the surface.
Reflectivity ρ: it is the fraction of irradiation reflected by the surface.
Transmissivity τ: it is the fraction of irradiation transmitted through the surface.
α+ρ+τ=1
Surface roughness decreases= Reflectivity decreases
Planks law of thermal radiation-
This law states that monochromatic emissive power of a body depends on both temperature and Web length of radiation.
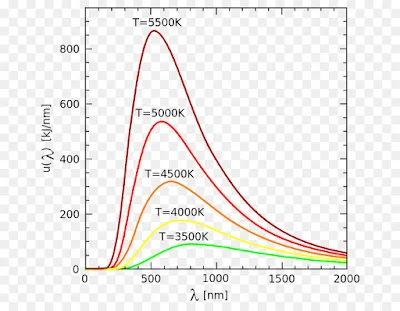
Wins displacement law-
After a long experiment, Wien found that the radiative energy dw per wavelength interval dλ has a maximum at a certain wavelength λm and that the maximum shifts to shorter wavelengths as the temperature T is increased
λmT= constant= 2898 micrometer kelvin
Click here to see











0 Comments
Thank for Visiting our site
we will Happy to see you here again